ME IT Placement
1)GOA or PONDI
You have just finished your semester and various departments are organizing their treks and trips for freshers to enjoy their first real break. Since most students have been trapped during the past months due to the pandemic, they are over excited and have registered for both the trip to Pondicherry and the trip to Goa.
However, overwhelming participation numbers have forced the council to limit each student to choosing only one option. The students who had selected both options have to be sent a mail to de-register from any one option.
You are part of our department council and are given List A corresponding to the roll numbers (a1,a2,...an) of the n students who have registered for the Pondi and List B corresponding to the roll numbers (b1,b2,...bm) of m students who have registered for the Goa. Prepare the mailing list by finding students common in both lists.
Input Format
The first line contains n , m The next two lines contain (a1,a2,...an) and (b1,b2,...bm) respectively as space separated integers
Constraints

Output Format
Space separated integers corresponding to roll numbers of students common in both lists arranged in ascending order.
Sample Input 0
8 8
729808343 482755096 19928028 818157287 408864491 214167585 739068537 135885045
934893737 135885045 591710214 10015942 408864491 773871948 215848179 482755096
Sample Output 0
135885045 408864491 482755096
Sample Input 1
20 20
48926690 449971594 591668725 869221903 774091841 347339341 278720164 988475670 844768341 497426572 127472441 123448213 17337391 797397565 924045423 73339738 694831669 982053373 203085446 616219719
340737465 616219719 931583899 982053373 511799849 73339738 73795327 797397565 732747662 123448213 60275291 497426572 624875617 988475670 503412607 347339341 851799710 869221903 92475833 449971594
Sample Output 1
73339738 123448213 347339341 449971594 497426572 616219719 797397565 869221903 982053373 988475670 Bear and Steady Gene
A gene is represented as a string of length (where is divisible by ), composed of the letters , , , and . It is considered to be steady if each of the four letters occurs exactly times. For example, and are both steady genes.
Bear Limak is a famous biotechnology scientist who specializes in modifying bear DNA to make it steady. Right now, he is examining a gene represented as a string . It is not necessarily steady. Fortunately, Limak can choose one (maybe empty) substring of and replace it with any string of the same length.
Modifying a large substring of bear genes can be dangerous. Given a string , can you help Limak find the length of the smallest possible substring that he can replace to make a steady gene?
Note: A substring of a string is a subsequence made up of zero or more contiguous characters of .
As an example, consider . The substring just before or after can be replaced with or . One selection would create .
Function Description
Complete the function in the editor below. It should return an integer that represents the length of the smallest substring to replace.
steadyGene has the following parameter:
- gene: a string
Input Format
The first line contains an interger divisible by , that denotes the length of a string .
The second line contains a string of length .
Constraints
- is divisible by
Subtask
- in tests worth points.
Output Format
Print the length of the minimum length substring that can be replaced to make stable.
Sample Input
8
GAAATAAA
Sample Output
5
Explanation
One optimal solution is to replace with resulting in .
The replaced substring has length .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string ltrim(const string &);
string rtrim(const string &);
/*
* Complete the 'steadyGene' function below.
*
* The function is expected to return an INTEGER.
* The function accepts STRING gene as parameter.
*/
int steadyGene(string gene) {
}
int main()
{
ofstream fout(getenv("OUTPUT_PATH"));
string n_temp;
getline(cin, n_temp);
int n = stoi(ltrim(rtrim(n_temp)));
string gene;
getline(cin, gene);
int result = steadyGene(gene);
fout << result << "\n";
fout.close();
return 0;
}
string ltrim(const string &str) {
string s(str);
s.erase(
s.begin(),
find_if(s.begin(), s.end(), not1(ptr_fun<int, int>(isspace)))
);
return s;
}
string rtrim(const string &str) {
string s(str);
s.erase(
find_if(s.rbegin(), s.rend(), not1(ptr_fun<int, int>(isspace))).base(),
s.end()
);
return s;
}
Boycott Assignments
Online semester is really hectic and you failed to keep pace with the lectures and assignment deadlines. You have a lot of assignments pending but only n slots to work. You decide to work for atleast k sessions of the same time duration. You like to sit for long sessions and so decided to keep the sessions as long as possible. Determine the longest possible duration of the session.
For example -
The value of n is 4 and the slots are of duration - [100,200,300,400]. and K is 10 . The maximum length of the session that is possible is 100 by taking [1,2,3,4] sessions on the respective slots. It is easy to see that if length>100, then you can't have sessions 10 sessions.
Hints -
- Devise an algorithm to check if the session length is t , will it be possible to complete all the assignments in k sessions?
- You may want to google "How to print 6 decimal places?". For C++, you can use setprecision.
Input Format
The first line contains two integers n and k. The next line contains n space separated integers - the duration of the available slot i given by ai
Constraints
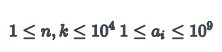
Output Format
Output one real number, the duration of the session truncated to the 6th decimal place.
Sample Input 0
3 20
97 95 98
Sample Output 0
13.857143
Sample Input 1
9 8
40 97 95 72 55 21 28 32 92
Sample Output 1
46.000000
Sample Input 2
8 15
91 56 26 53 10 44 64 11
Sample Output 2
18.666667Poisonous Plants
There are a number of plants in a garden. Each of the plants has been treated with some amount of pesticide. After each day, if any plant has more pesticide than the plant on its left, being weaker than the left one, it dies.
You are given the initial values of the pesticide in each of the plants. Determine the number of days after which no plant dies, i.e. the time after which there is no plant with more pesticide content than the plant to its left.
Example
// pesticide levels
Use a -indexed array. On day , plants and die leaving . On day , plant in dies leaving . There is no plant with a higher concentration of pesticide than the one to its left, so plants stop dying after day .
Function Description
Complete the function poisonousPlants in the editor below.
poisonousPlants has the following parameter(s):
- int p[n]: the pesticide levels in each plant
Returns
- int: the number of days until plants no longer die from pesticide
Input Format
The first line contains an integer , the size of the array .
The next line contains space-separated integers .
Constraints
Sample Input
7
6 5 8 4 7 10 9
Sample Output
2
Explanation
Initially all plants are alive.
Plants = {(6,1), (5,2), (8,3), (4,4), (7,5), (10,6), (9,7)}
Plants[k] = (i,j) => jth plant has pesticide amount = i.
After the 1st day, 4 plants remain as plants 3, 5, and 6 die.
Plants = {(6,1), (5,2), (4,4), (9,7)}
After the 2nd day, 3 plants survive as plant 7 dies.
Plants = {(6,1), (5,2), (4,4)}
Plants stop dying after the 2nd day.
Plants stop dying after the 2nd day.
Demanding Money
Killgrave wants to use his mind control powers to get money from the Justice League superheroes living in houses in Happy Harbor that are numbered sequentially from to . There are roads, and each road connects two different houses, and . Each superhero house (where ) has dollars stashed away for a rainy day.
As long as a superhero is home at house , Killgrave knows they will hand over all of their saved money, . Once he gets money from them, he moves on to the next house. However, the superheroes are cunning; when Killgrave comes to house , every neighbor immediately connected to house by a single road skips town for a couple of days (making it impossible for Killgrave to get money from them). In other words, after Killgrave visits all the superheroes he wants, there will be no road in which he was able to get money from both houses on either end of the road.
What is the maximum amount of money Killgrave can collect from the superheroes, and how many different ways can Killgrave get that amount of money? Two ways are considered to be different if the sets of visited houses are different.
Note: Killgrave can start at an arbitrary house and doesn't have to only use the roads.
Input Format
The first line contains two space-separated integers, (the number of houses) and (the number of roads), respectively.
The second line contains space-separated integers, where each integer describes the amount of money, , at house .
Each line of the subsequent lines contains two space-separated integers defining a road connecting houses and . Every road connects a different pair of houses.
Constraints
- , where
- No unordered pair will appear more than once.
Output Format
Print two space-separated integers:
- The first integer must denote the maximum amount of money Killgrave can get out of the Justice League.
- The second integer must denote the number of different ways he can collect that amount of money.
Sample Input
3 2
6 8 2
1 2
3 2
Sample Output
8 2
Explanation

Killgrave has two possible courses of action:
- Visit house and get dollars.
- Visit houses and and get dollars.
Both of these options result in dollars, so we know that this is maximal. Thus, we print the maximum amount of money () followed by the number of ways he can get that amount of money () as two space-separated values on a single line.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string ltrim(const string &);
string rtrim(const string &);
vector<string> split(const string &);
/*
* Complete the 'demandingMoney' function below.
*
* The function is expected to return an INTEGER_ARRAY.
* The function accepts following parameters:
* 1. INTEGER_ARRAY money
* 2. 2D_INTEGER_ARRAY roads
*/
vector<int> demandingMoney(vector<int> money, vector<vector<int>> roads) {
}
int main()
{
ofstream fout(getenv("OUTPUT_PATH"));
string first_multiple_input_temp;
getline(cin, first_multiple_input_temp);
vector<string> first_multiple_input = split(rtrim(first_multiple_input_temp));
int n = stoi(first_multiple_input[0]);
int m = stoi(first_multiple_input[1]);
string money_temp_temp;
getline(cin, money_temp_temp);
vector<string> money_temp = split(rtrim(money_temp_temp));
vector<int> money(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int money_item = stoi(money_temp[i]);
money[i] = money_item;
}
vector<vector<int>> roads(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
roads[i].resize(2);
string roads_row_temp_temp;
getline(cin, roads_row_temp_temp);
vector<string> roads_row_temp = split(rtrim(roads_row_temp_temp));
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
int roads_row_item = stoi(roads_row_temp[j]);
roads[i][j] = roads_row_item;
}
}
vector<int> result = demandingMoney(money, roads);
for (size_t i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
fout << result[i];
if (i != result.size() - 1) {
fout << " ";
}
}
fout << "\n";
fout.close();
return 0;
}
string ltrim(const string &str) {
string s(str);
s.erase(
s.begin(),
find_if(s.begin(), s.end(), not1(ptr_fun<int, int>(isspace)))
);
return s;
}
string rtrim(const string &str) {
string s(str);
s.erase(
find_if(s.rbegin(), s.rend(), not1(ptr_fun<int, int>(isspace))).base(),
s.end()
);
return s;
}
vector<string> split(const string &str) {
vector<string> tokens;
string::size_type start = 0;
string::size_type end = 0;
while ((end = str.find(" ", start)) != string::npos) {
tokens.push_back(str.substr(start, end - start));
start = end + 1;
}
tokens.push_back(str.substr(start));
return tokens;
}
Array Pairs
Consider an array of integers, . Find and print the total number of pairs such that where .
Input Format
The first line contains an integer, , denoting the number of elements in the array.
The second line consists of space-separated integers describing the respective values of .
Constraints
Scoring
- for of the test cases.
- for of the test cases.
- for of the test cases.
Output Format
Print a long integer denoting the total number pairs satisfying where .
Sample Input
5
1 1 2 4 2
Sample Output
8
Explanation
There are eight pairs of indices satisfying the given criteria: , , , , , , , and . Thus, we print as our answer.
bbb
cc
Comments
Post a Comment